Most health experts agree that early and aggressive treatment for COVID-19 helps to reduce the potential for long COVID symptoms and reduces the risk of severe disease. From the beginning, the pharmaceutical industry has sought to develop new and expensive antiviral drugs to treat the coronavirus responsible for COVID-19 with an aim at profits. The newest drug — monoclonal antibody treatment bebtelovimab from Eli Lilly1 — is no exception.
For example, Dr. Anthony Fauci’s favorite drug used early in the pandemic on hospitalized patients — remdesivir — cost the taxpayers over $70.5 million to develop.2 A five-day course of treatment costs private insurance companies $3,120 and the government $2,340,3 which is doubled at $6,240 for private companies and $4,680 for the government for a 10-day course.
This is well above the drug maker’s estimated cost for production, which is between $10 and $600 for a 10-day course.4 Fauci, who is the director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease (NIAID), has been the face of the public health initiatives against COVID since the pandemic was announced by the World Health Organization in March 2020.
In the first year or more of the pandemic, patients were told to suffer at home until they were near death and then go to the hospital where they were placed on deadly ventilator treatment.5,6
In my interview with Dr. Pierre Kory,7 one of the leaders in the movement to provide early treatment for COVID infection, he recalled how he refused to remain in leadership at the University of Wisconsin Medical Center where the hospital insisted on providing supportive care only to their patients.8
However, as the pharmaceutical industry has released a variety of drugs or treatments, including monoclonal antibodies, Paxlovid and remdesivir, the perspective has changed.
Hospitals and physicians now offer pharmaceutical treatments approved under emergency use authorization (EUA) with unknown long-term side effects but continue to refuse to use well-established drugs with known side effect profiles that have proven to be effective. Hydrogen peroxide is one of those preventive measures and treatments.
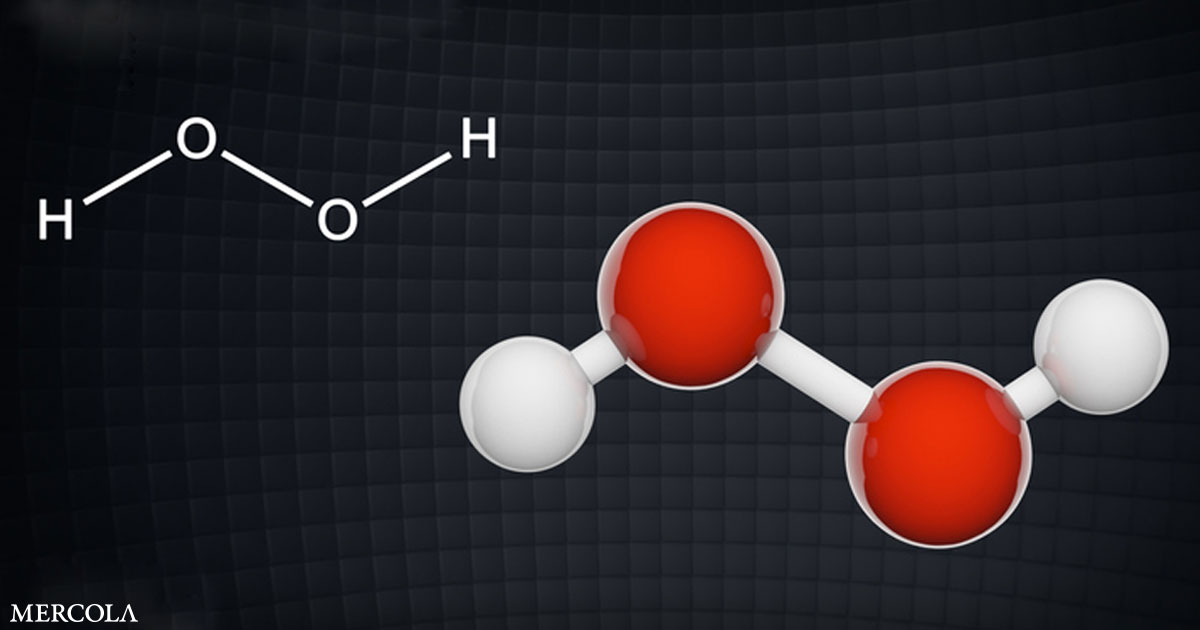
Hospital Study Shows H2O2 Prevents COVID-19
In August 2022, a study9,10 of over 4,000 patients and 89 health care staff in a hospital in Ghana revealed the results of those who used hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) mouthwash, gargle and nasal rinse daily as a preventive against COVID-19.11
The researchers compared the data between two hospitals in Ghana where individuals who were vaccinated or not vaccinated either used H2O2 prophylactically or did not. The effect on inpatients was also recorded. They found that in the 89 health care staff members who used the H2O2 preventively, only one contracted COVID-19 and that person had discontinued using the rinses.
None of the greater than 4,000 patients who were treated with H2O2 got COVID-19. In another hospital, 424 staff members were fully vaccinated; 34 of those used hydrogen peroxide and none developed COVID-19. Of the remaining 390 health care staff, 53 developed COVID-19.
In another group of 78 unvaccinated staff, 23 used hydrogen peroxide and none of them contracted COVID-19. In the remaining group, 35 got COVID-19. The results from this study suggested that H2O2 was more effective at preventing COVID-19 than the jab.
The participants used 1% hydrogen peroxide mouthwash and diluted hydrogen peroxide to 0.5% for the nasal cavity rinse. The treatment was done only once daily.
The researchers concluded, “Regular, daily HPA [hydrogen peroxide antisepsis] protects HCWs [health care workers] from COVID-19 and curtails nosocomial spread of SARS-CoV-2.”12 This is important since infections in the hospital are more easily transmitted when staff have greater face-to-face exposure with patients and each other.
The data from the August 22 study confirmed an earlier observational report13 by the same team on two groups of health care workers. In the earlier results, the researchers found that 89 of 944 health care workers who did not use hydrogen peroxide tested positive for COVID-19 in the study period. During the same time, 154 health care workers used the hydrogen peroxide treatment and 100% of those tested negative.
A Nebulizer Drives the Hydrogen Peroxide Even Deeper
In April 2021, I interviewed Dr. Thomas Levy,14 board-certified cardiologist who is best known for his work with vitamin C. We discussed the use of nebulized hydrogen peroxide, which has become my favorite intervention for the treatment and prevention of viral illnesses.
H2O2 is part of your body’s natural defense system, so using nebulized H2O2 just augments your body’s natural defense system. However, as I discuss in the video above, it’s essential that you mix the solution appropriately, use normal saline to protect your lung tissue and use the treatment until all the fluid in the chamber has evaporated, often taking approximately 30 minutes.
Nebulized hydrogen peroxide also requires the use of a food-grade product that does not have the stabilizers and chemical preservatives found in the H2O2 bottle on drugstore shelves. It is also important to use distilled water or saline, since tap water can contain a deadly amoeba.15 Your gastrointestinal tract can adequately take care of this pathogen but inhaling it into your lungs can cause significant damage.
One of the benefits of nebulizing hydrogen peroxide is that it disperses the H2O2 throughout your mouth, nasal cavity, sinuses, throat and lungs. This is especially powerful if you have been exposed to a viral illness or are sick.
Nebulized H2O2 can help kill viral particles in your respiratory tract but does not reach any viral particles in the rest of your body. Therefore, using nebulized H2O2 after exposure or in the early hours of a respiratory infection may help stop an infection in its tracks.
If you miss the early window to prevent an infection, using the treatment also helps to protect your lungs from developing pneumonia, which can be deadly in those with COVID-1916,17 or flu.18
Taxpayers Spend $1,833 per Dose on Monoclonal Antibody Drug
In February 2022, the FDA19 approved an EUA for a new monoclonal antibody treatment for the COVID-19 omicron variant. The drug — bebtelovimab — was developed by Eli Lilly. The government immediately ordered 600,000 doses, spending $1.08 billion or $1,800 per dose.20 According to Endpoint News,21 another order for 150,000 doses was approved for $275 million, the equivalent of $1,833 per dose.
The $33 per dose increase in price occurred in just four months. While this may not sound like a lot of money for a single dose, spread over 150,000 doses it means the U.S. taxpayers shelled out an extra $4.9 million for the same drug just four months later.
According to the announcement by the FDA,22 the EUA was approved for the treatment of mild to moderate infection in adults and children 12 years of age and older who are at least 88 pounds. The individuals must have a positive COVID-19 test and have indications that they are:
“… at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death, and for whom alternative COVID-19 treatment options approved or authorized by the FDA are not accessible or clinically appropriate.”
In other words, for an illness that has a track record of 99% recovery,23 the U.S. government has thus far spent $1.35 billion on 750,000 doses of a drug that by the FDA’s own evaluation should only be used for individuals who are at high risk of severe COVID-19.
According to CDC data24 there were a total of slightly over 1 million deaths from COVID-19 over a 2.5-year period. However, as even the CDC has admitted, many of the deaths attributed to COVID-19 have actually been people died WITH COVID-19, not FROM it.
One of the more infamous cases of death certificates recording a COVID death was from a motorcycle accident,25 which may have been following the CDC’s own guideline for reporting deaths:26
“In cases where a definite diagnosis of COVID cannot be made but is suspected or likely (e.g. the circumstances are compelling with a reasonable degree of certainty) it is acceptable to report COVID-19 on a death certificate as ‘probable’ or ‘presumed.'”
As has been widely reported, while the omicron virus is more transmissible, it is also less virulent and doesn’t cause the severe illness that the variants before it.27 Additionally, if the government drinks their own Kool-Aid, those who are vaccinated are protected from severe disease.28
Thus, there should be no need for 750,000 doses of a monoclonal antibody that should only be prescribed to those at “high risk”29 of severe illness. Added to this, Drugs.com reports, “Not many people have received bebtelovimab. Serious and unexpected side effects may happen. All of the risks are not known at this time.”30
Rebound Illness After Antiviral Paxlovid
Fierce Pharma31 reported that Pfizer also scored a huge deal when the U.S. doubled their order for the antiviral Paxlovid from 10 million to 20 million courses of treatment. The first 10 million cost the U.S. taxpayers $5.29 billion and contributed to Pfizer’s anticipated revenue of $101.3 billion in 2022.
Fierce Pharma32 also reported that one analyst, writing to clients, reported that Paxlovid had a “leg up” on molnupiravir because of its “superior efficacy and safety profile.”
Paxlovid joins a long list of drugs developed specifically for COVID-19 that have not proven to be effective. Reports are emerging33 that patients treated with a five-day course will sometimes experience severe rebound when the course is completed. Government officials are planning to study the rate of rebound, the extent to which the drug causes rebound and whether a longer regimen will reduce the effect.
Virologist David Ho described the post-Paxlovid rebound he experienced in April to Bloomberg.34 After getting sick, his doctor prescribed Paxlovid. Days later his symptoms dissipated, and the tests were negative. However, 10 days after getting sick, the symptoms returned and the tests were positive again.
He sequenced the virus in his body and found that the infection before and after taking Paxlovid were from the same strain, confirming that the virus didn’t mutate or become resistant to the drug. Pfizer, meanwhile, insists the increase in viral load post-treatment “is unlikely to be related to Paxlovid” because viral rebound was found in “a small number” of both the treatment and placebo groups in Pfizer’s final-stage study.35
Subsequently, quadruple-vaccinated Fauci reported that he tested positive for COVID-19 and experienced mild symptoms.36 Reportedly his age placed him at high risk for complications and he was then prescribed Paxlovid.37 CNN reported he described the “interesting course” of his COVID-19 infection during an appearance at Foreign Policy’s Global Health Forum.
Fauci told the group that after five days he was negative for three consecutive days on an antigen test. Apparently, three negative tests weren’t enough, so he tested himself again on the fourth day “just to be absolutely certain.” By that time, he had reverted to a positive test. “It was sort of what people are referring to as a Paxlovid rebound,” he said.38
Low Cost, Low Side Effect, Effective Treatment Available
Fauci reported that his symptoms were worse when they returned the second time after treatment. He was prescribed another course of Paxlovid and at the time of the interview, he was on day 4 of a 5-day course. He reportedly felt “reasonably good” although “not completely without symptoms.”39
The cost of Paxlovid can be as much as $53040 for a five-day course, but consumers get it for “free” since it was purchased with their tax dollars. During these past two years, the government has spent billions of dollars buying medication for an infectious illness that has been proven to be successfully treated at home using far less expensive medications and supplements.
For example, the overall survival rate across all age groups and all risk strata is 99%, but the Zelenko Protocol41 has demonstrated a 99% survival rate in high-risk patients. His published treatment protocol includes over-the-counter supplements vitamins C and D3, elemental zinc and quercetin for low-risk patients.
Patients who have a moderate or high risk of severe disease are treated with vitamin C and D3, elemental zinc, azithromycin, doxycycline, hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin.
The Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance42 has developed several protocols43 aimed at prevention, early treatment, long-haul COVID treatment, post-vaccine recovery and hospital treatment. First-line therapies in early treatment include over-the-counter zinc, vitamin C, melatonin, quercetin, probiotics, curcumin, aspirin, mouthwash and nasal spray. Prescription medications include ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine.
Both protocols are highly successful with known side effect profiles since the medications and supplements have been used for many years. Both protocols are based on the premise that early treatment can reduce the risk of long-haul COVID symptoms and the potential to develop severe disease. Most of the therapies are inexpensive and easily purchased over the counter.
The Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance44 also maintains a list of physicians who follow the protocols and provide in-office and telehealth services. I believe one of the most powerful strategies you can use preventively and in early treatment is nebulized hydrogen peroxide.
As the featured study demonstrated, even with store-bought hydrogen peroxide diluted for nasal wash, mouthwash and gargling once daily, you can effectively prevent infection. Although health authorities would like to limit your treatment choices and keep you chained to new and not thoroughly tested drugs where “all the risks are not known at this time,”45 you have choices and can take control of your health.